meteorite: a solid piece of debris from an object that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon.
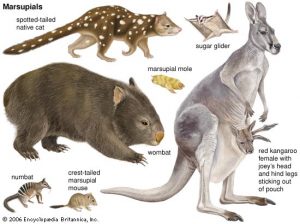
marsupials: marsupials are endemic to Australasiaand the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to these species is that most of the young are carried in a pouch. Well-known marsupials include kangaroos, wallabies, koalas, etc.
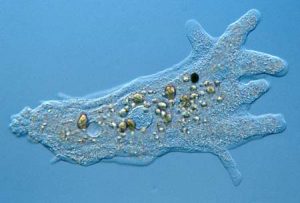
amoebas: a type of cell or organism which has the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals.
University of California in San Diego: a public research university located in the La Jolla neighborhood of San Diego, California, in the United States
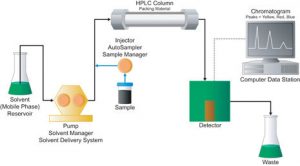
liquid chromotagraphy: a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture of liquids. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid called the mobile phase, which carries it through a structure holding another material called the stationary phase. The various constituents of the mixture travel at different speeds, causing them to separate
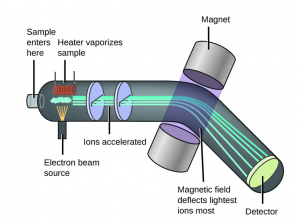
mass spectrometry: an analytical technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio in order to measure the masses within a sample
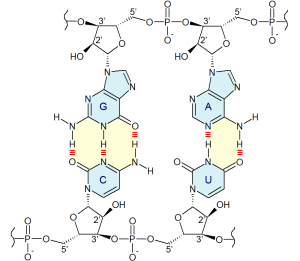
nucleobases: nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which are components of nucleotides, which are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such as RNA and DNA.
Bach’s Tocata and Fugue in D Minor: a piece of organ music written, according to its oldest extant sources, by Johann Sebastian Bach. The piece opens with a toccata section, followed by a fugue that ends in a coda. It is one of the most famous works in the organ repertoire.


You must be logged in to post a comment.