The US began looking into North Korea’s computer network in 2010, reports claim
Category Archives: Cyber Espionage
British Spy Agency Captured Journalists’ Messages Amongst 70,000 E-mails
The Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), the British sister agency of the National Security Agency, captured e-mails of some journalists out of 70,000 message intercepted in 10 minutes during a November 2008 test.
According to The Guardian, which on Monday cited some of its Snowden documents as its source (but did not publish them), the e-mails were scooped up as part of the intelligence agency’s direct fiber taps.
Journalists from the BBC, Reuters, The Guardian, The New York Times, Le Monde, The Sun, NBC, and The Washington Post were apparently targeted.
Read 2 remaining paragraphs | Comments
US (Sort of) Points to “Smoking Gun” Linking North Korea to Sony Hack
Citing anonymous sources in and close to the US government, The New York Times reports that the fingering of North Korea as responsible for the attack on the network of Sony Pictures Entertainment was through evidence gathered by National Security Agency surveillance. This includes software taps into networks associated with North Korea’s network warfare and espionage unit, Bureau 121, among others. The actual evidence, however, will likely never see the light of day because of the highly classified nature of how it was obtained.
David Sanger and Martin Fackler of the Times report that the NSA started to ramp up efforts to penetrate North Korea’s networks in 2010 to monitor the growth of Bureau 121 and the rest of the country’s “computer network exploitation” capabilities:
A classified security agency program expanded into an ambitious effort, officials said, to place malware that could track the internal workings of many of the computers and networks used by the North’s hackers, a force that South Korea’s military recently said numbers roughly 6,000 people. Most are commanded by the country’s main intelligence service, called the Reconnaissance General Bureau, and Bureau 121, its secretive hacking unit, with a large outpost in China.
The evidence gathered by the “early warning radar” of software painstakingly hidden to monitor North Korea’s activities proved critical in persuading President Obama to accuse the government of Kim Jong-un of ordering the Sony attack, according to the officials and experts, who spoke on the condition of anonymity about the classified NSA operation.
The NSA’s Tailored Access Office, according to the report, “drilled into the Chinese networks that connect North Korea to the outside world, picked through connections in Malaysia favored by North Korean hackers, and penetrated directly into the North with the help of South Korea and other American allies.” According to NSA documents released by Der Spiegel, some of South Korea’s initial assistance was not voluntary—the NSA secretly exploited South Korea’s existing hacks of North Korea to gain intelligence information. But despite the level of access they gained, according to an unnamed investigator into the Sony Pictures attack, the NSA and other US agencies “couldn’t really understand the severity” of the attack that would be launched against Sony when they began on November 24.
Read on Ars Technica | Comments
Jet Data Theft ‘Shows Cyber-Spy Risk’
The reported theft by Chinese spies of designs for Australia’s new warplane, the US-built F-35 Joint Strike Fighter jet, highlights cyber-espionage risks, Australia’s FM says.
NSA Secretly Hijacked Existing Malware to Spy on N. Korea, Others
A new wave of documents from Edward Snowden’s cache of National Security Agency data published by Der Spiegel demonstrates how the agency has used its network exploitation capabilities both to defend military networks from attack and to co-opt other organizations’ hacks for intelligence collection and other purposes. In one case, the NSA secretly tapped into South Korean network espionage on North Korean networks to gather intelligence.
The documents were published as part of an analysis by Jacob Appelbaum and others working for Der Spiegel of how the NSA has developed an offensive cyberwarfare capability over the past decade. According to a report by the New York Times, the access the NSA gained into North Korea’s networks—which initially leveraged South Korean “implants” on North Korean systems, but eventually consisted of the NSA’s own malware—played a role in attributing the attack on Sony Pictures to North Korean state-sponsored actors.
Included with the documents released by Der Spiegel are details on how the NSA built up its Remote Operations Center to carry out “Tailored Access Operations” on a variety of targets, while also building the capability to do permanent damage to adversaries’ information systems, including internal NSA newsletter interviews and training materials. Also included was a malware sample for a keylogger, apparently developed by the NSA and possibly other members of the “Five Eyes” intelligence community, which was also included in the dump. The code appears to be from the Five Eyes joint program “Warriorpride,” a set of tools shared by the NSA, the United Kingdom’s GCHQ, the Australian Signals Directorate, Canada’s Communications Security Establishment, and New Zealand’s Government Communications Security Bureau.
Read 8 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Surprise! North Korea’s Official News Site Delivers Malware, Too
A security researcher examining the website of North Korea’s official news service, the Korean Central News Agency, has discovered that the site delivers more than just the latest photo spread of Democratic Peoples’ Republic of Korea leader Kim Jong Un inspecting mushroom farms. There’s a little extra surprise hidden in the site’s code—malware. The news site appears to double as a way for North Korea to deliver a “watering hole” attack against individuals who want to keep tabs on the “activities” of the DPRK’s dear leader.
Ars has independently verified a reference within part of the site’s JavaScript code called from the home page to a download named “FlashPlayer10.zip.” The file, which is set as a JavaScript variable “FlashPlayer” on the site’s main page and on other site pages, contains two files labeled as Windows executable installers containing updates for the long-since obsolete Flash Player 10—one for an alleged ActiveX control, and the other for a browser plug in. Both are identical files, and they contain a well-known Windows malware dropper, based on an analysis through the malware screening site Virustotal.
Read 3 remaining paragraphs | Comments
FBI Director says Sony Hackers “Got Sloppy,” Exposed North Korea Connection [Updated]
In a speech at the International Conference on Cyber Security (ICCS) today in New York, FBI Director James Comey reiterated the bureau’s confidence that North Korea was involved in the cyber attack on Sony Pictures Entertainment. “There’s not much I have high confidence about,” Comey said, as reported by the FBI New York field office’s official Twitter feed. “I have very high confidence… on North Korea.” And he downplayed suggestions by outsiders that others might be responsible, saying that critics “don’t have the facts that I have, they don’t see what I see.”
In a separate speech today at the ICCS, Director of National Intelligence James Clapper said that the attack on Sony demonstrated a new type of threat posed by North Korea. During a meeting last year with a North Korean general to negotiate the release of two American prisoners in North Korea, Clapper said that the general told him the regime is “deadly serious” about perceived insults by the US to its “supreme leader” and that North Koreans feel that the US has put their country under siege.
While the Sony attackers had largely concealed their identity by using proxy servers, Comey said that on several occasions they “got sloppy” and connected directly, revealing their own IP address. It was those slip-ups, he said, that provided evidence linking North Korea to the attack on Sony’s network. Comey also said that analysts at the FBI found the patterns of writing and other identifying data from the attack matched previous attacks attributed to North Korea. Additionally, there was other evidence, Comey said, that he could not share publicly.
Read 3 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Phishing Scam That Penetrated Wall Street Just Might Work Against You, Too
Researchers have uncovered a group of Wall Street-savvy hackers that has penetrated the e-mail accounts of more than 100 companies, a feat that has allowed them to obtain highly valuable plans concerning corporate acquisitions and other insider information.
FIN4, as the group is known, relies on a set of extremely simple tactics that in many cases has allowed them to remain undetected since at least the middle of 2013, according to a report published Monday from security firm FireEye. Members boast a strong command of the English language and knowledge of corporate finance and Fortune 500 culture. They use that savvy to send highly targeted spearphishing e-mails that harvest login credentials for Microsoft Outlook accounts. The group then uses compromised accounts of one employee, customer, or partner to send spearphishing e-mails to other company insiders. At times, the attackers will inject a malicious message into an ongoing e-mail discussion among multiple people, furthering their chances of success.
E-mails are sent from the accounts of people the target knows, and they discuss mergers, acquisitions, or other topics already in progress. The attackers often bcc other recipients to make it more difficult to detect the malicious e-mail. The messages appear to be written by native English speakers and often contain previously exchanged Microsoft Office documents that embed hidden malicious macros. This results in fraudulent e-mails that are extremely hard to detect, even by some people who have been trained to spot such phishing campaigns. Witness the following:
Read 6 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Researchers Uncover Government Spy Tool Used to Hack Telecoms and Belgian Cryptographer

Piecing together new information from various researchers, it’s clear the ‘Regin” malware is one of the most sophisticated nation-state spy tools ever found.
The post Researchers Uncover Government Spy Tool Used to Hack Telecoms and Belgian Cryptographer appeared first on WIRED.
![]()
Highly Advanced Backdoor Trojan Cased High-profile Targets for Years
Researchers have unearthed highly advanced malware they believe was developed by a wealthy nation-state to spy on a wide range of international targets in diverse industries, including hospitality, energy, airline, and research.
Backdoor Regin, as researchers at security firm Symantec are referring to the trojan, bears some resemblance to previously discovered state-sponsored malware, including the espionage trojans known as Flame and Duqu, as well as Stuxnet, the computer worm and trojan that was programmed to disrupt Iran’s nuclear program. Regin likely required months or years to be completed and contains dozens of individual modules that allowed its operators to tailor the malware to individual targets.
To remain stealthy, the malware is organized into five stages, each of which is encrypted except for the first one. Executing the first stage triggers a domino chain in which the second stage is decrypted and executed, and that in turn decrypts the third stage, and so on. Analyzing and understanding the malware requires researchers to acquire all five stages. Regin contains dozens of payloads, including code for capturing screenshots, seizing control of an infected computer’s mouse, stealing passwords, monitoring network traffic, and recovering deleted files. Other modules appear to be tailored to specific targets. One such payload included code for monitoring the traffic of a Microsoft IIS server. Another sniffed the traffic of mobile telephone base station controllers.
Read 4 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Obama Will Likely Enact Panel’s Advice on Blunting Cyber Risks
Six Journalists Sue Over Surveillance by UK “Extremist” Police Unit
Six members of the United Kingdom’s National Union of Journalists—including comedian and journalist Mark Thomas—have filed suit against London’s Metropolitan Police after discovering that their daily activities were being monitored and recorded in a police database. The database is gathered by the National Domestic Extremists and Disorder Intelligence Unit, a task force led by the Metropolitan Police Service that tracks political and religious groups in the UK and monitors protests.
In an interview on BBC Radio 4, Thomas said that the surveillance was discovered through information uncovered by a request under the UK’s Data Protection Act—a law similar to the US’ Freedom of Information Act. “The police are gathering information under the domestic extremist list about journalist and NUJ members, “ he said. “And we know this because six of us have applied to the police using the Data Protection Act to get some of the information the police are holding on us on these lists. And what they are doing is monitoring journalists’ activities and putting them under surveillance and creating databases about them.”
Thomas has used the Data Protection Act in the name of both journalism and comedy. In 2001, he launched a contest in which he encouraged people to do creative performances in front of surveillance cameras and then submit the videos to him after obtaining them through Data Protection Act requests.
Read 2 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Feds Proposed the Secret Phone Database Used by Local Virginia Cops
A Virginia-based law enforcement data sharing ring, which allows signatory police agencies to share and analyze seized “telephone intelligence information,” was first proposed by federal prosecutors, according to new documents obtained by Ars. Federal involvement suggests that there could be more such databases in other parts of the country.
“It’s unsurprising to see the feds encouraging local law enforcement agencies to create these localized databases,” Hanni Fakhoury, a staff attorney with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, told Ars. “In fact, there’s a whole division within the Department of Justice that focuses on educating and advancing local law enforcement interests, the National Institute of Justice. And so I would imagine there are others.”
As Ars reported last month, according to a memorandum of understanding (MOU) first published by the Center for Investigative Reporting, the police departments from Hampton, Newport News, Norfolk, Chesapeake, and Suffolk all participate in something called the “Hampton Roads Telephone Analysis Sharing Network,” or HRTASN.
Read 20 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Amnesty Releases Anti-spying Program
Amnesty International has released a program that can spot spying software used by governments to monitor activists and political opponents.
Critical NSA Reform Bill Fails in the Senate

Tonight, the lame duck senate still run by the democrats voted on the USA Freedom Act, a bipartisan-backed bill to usher in NSA reform.
The post Critical NSA Reform Bill Fails in the Senate appeared first on WIRED.
![]()
State Department Targeted by Hackers in 4th Agency Computer Breach
Soldiers, Spies, Cyberwarriors: ‘@War’ In The Internet Age
“One if by land, two if by sea” wouldn’t work these days — not when your adversary can knock out your power grid with an team of cyberforces. Today’s armies have a new front to monitor.
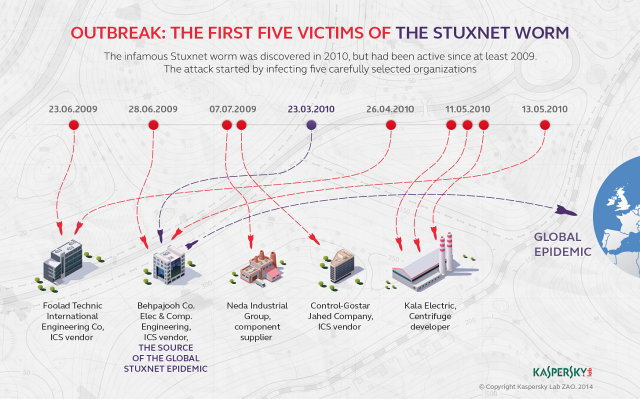
Stuxnet Worm Infected High-Profile Targets before Hitting Iran Nukes
The Stuxnet computer worm that attacked Iran’s nuclear development program was first seeded to a handful of carefully selected targets before finally taking hold in uranium enrichment facilities, according to a book published Tuesday.
The new account, included in Countdown to Zero Day: Stuxnet and the Launch of the World’s First Digital Weapon by Wired reporter Kim Zetter, is at odds with the now-popular narrative that the malware first penetrated Iran’s Natanz enrichment facility and later unexpectedly broke loose to infect hundreds of thousands of other sites across the globe. That earlier account, provided by New York Times journalist David Sanger, characterized the escape outside of Natanz as a programming error that was never intended by engineers in the US and Israel, the two countries Sanger and Zetter said devised and unleashed Stuxnet. According to Zetter, the world’s first known cyber weapon first infected Iranian companies with close ties to Iranian nuclear facilities and only later found its way to Natanz.
“To get their weapon into the plant, the attackers launched an offensive against four companies,” Zetter wrote. “All of the companies were involved in industrial control processing of some sort, either manufacturing products or assembling components or installing industrial control systems. They were likely chosen because they had some connection to Natanz as contractors and provided a gateway through which to pass Stuxnet to Natanz through infected employees.”
Read 6 remaining paragraphs | Comments
DarkHotel: A Sophisticated New Hacking Attack Targets High-Profile Hotel Guests

The hotel guest probably never knew what hit him. When he tried to get online using his five-star hotel’s WiFi network, he got a pop-up alerting him to a new Adobe software update. When he clicked to accept the download, he got a malicious executable instead. What he didn’t know was that the sophisticated attackers […]
The post DarkHotel: A Sophisticated New Hacking Attack Targets High-Profile Hotel Guests appeared first on WIRED.
![]()
Is Your Car Spying on You?
Is the connected car a threat to data privacy?